News
Radiotherapy is emerging as an important modality for the local control of pancreatic cancer, but pancreatic cancer cell radioresistance remains a serious concern. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α (PPARα) is a member of the PPAR nuclear hormone receptor superfamily, which can be activated by fibrate ligands. The clinical relevance of PPARα and its biological function in pancreatic cancer radiosensitivity have not been previously described.
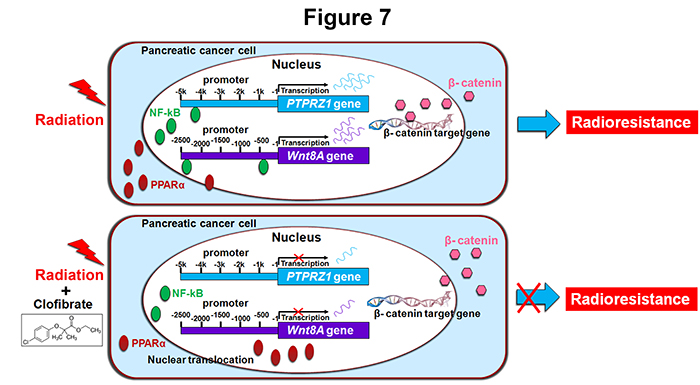
Researchers from the Center of Radiobiology found significantly higher expression of PPARα in pancreatic cancer tissues than in tumor-adjacent tissues, and that the PPARα expression level is inversely associated with higher overall patient survival rate. We further observed that PPARα activation by its agonist clofibrate sensitizes pancreatic cancer cells to radiation by modulating cell cycle progression and apoptosis in several pancreatic cancer cell lines. siRNA-mediated PPARα silencing and PPARα blockade by the antagonist GW6471 abolish the effect of clofibrate on radiosensitization. An in vivo study showed that PANC1 xenografts treated with clofibrate are more sensitive to radiation than untreated xenografts. mRNA profiling by microarray analysis revealed that expression of PTPRZ1 and Wnt8a, two core components of the β-catenin pathway, is downregulated by clofibrate. Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) analysis confirmed that clofibrate abrogates the binding of NF-κB to the PTPRZ1 and Wnt8a promoters, ultimately decreasing Wnt/β-catenin signaling activity, which is associated with radiosensitivity.
Overall, this study demonstrates that PPARα is overexpressed in pancreatic cancer tissues and clofibrate-mediated PPARα activation sensitizes pancreatic cancer cells to radiation through the Wnt/β-catenin pathway.